

23 out of 100 people reported treatment success with placebo.32 out of 100 people reported treatment success with vertebroplasty.
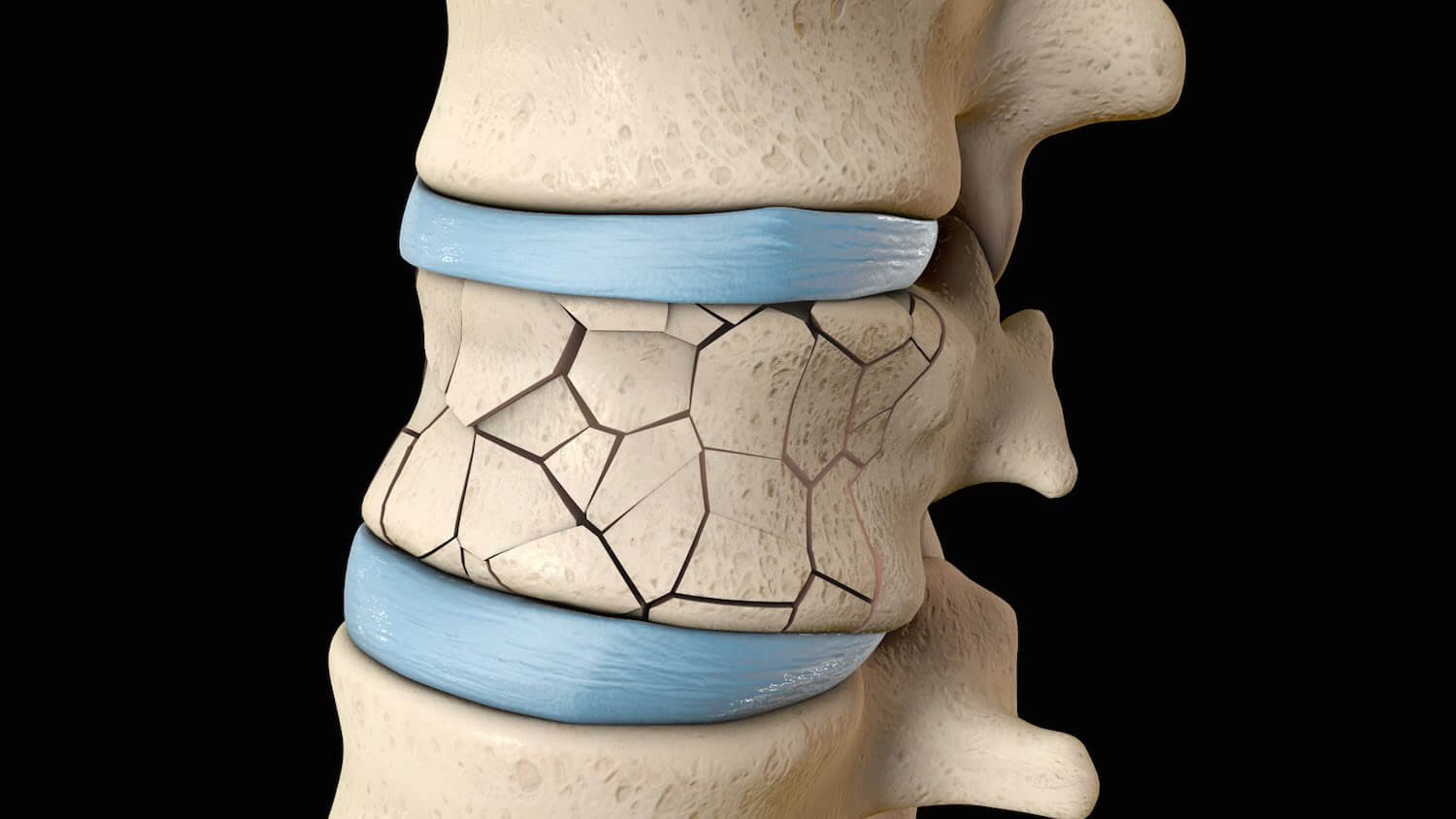
Treatment success (defined as pain moderately or a great deal better)ĩ% more people rated their treatment a success (11% fewer to 29% more), or nine more people out of 100. People who had placebo rated their general quality of life as 0.38 points.People who had vertebroplasty rated their general quality of life as 0.43 points.Improved by 5% (1% better to 9% better), or 0.05 units (0.01 better to 0.09 better) on a zero = death to one = perfect health scale. Overall quality of life (higher scores mean better quality of life) People who had placebo rated their quality of life related to their fracture as 62 points.People who had vertebroplasty rated their quality of life related to their fracture as 59.7 points.Vertebral fracture or osteoporosis-specific quality of life (lower scores mean better quality of life)īetter by 2% (1% worse to 6% better), or 2.33 points better (1.41 worse to 6.06 better) on a zero to 100-point scale. People who had placebo rated their disability as 14.2 points.People who had vertebroplasty rated their disability as 12.7 points.Improved by 7% (2% better to 11% better), or 1.5 points (0.4 better to 2.6 better) on a zero to 23-point scale. People who had placebo rated their pain as 5 points.ĭisability (lower scores mean less disability).People who had vertebroplasty rated their pain as 4.3 points.Improved by 7% (3% better to 12% better), or 0.7 points (0.3 better to 1.2 better) on a zero-0 to 10-point scale. Eight trials received at least some funding from medical device manufacturers and only two reported that they had no role in the trial.Ĭompared with a placebo (fake) procedure, vertebroplasty resulted in little benefit at one month: Trials were performed in hospitals in 15 countries, the majority of participants were female, mean age ranged between 63.3 and 80 years, and symptom duration ranged from a week to six months or more. Studies compared vertebroplasty versus placebo (no cement injected) (five studies, 541 participants) usual care (eight studies, 1136 participants) kyphoplasty (similar, but before cement is injected a balloon is expanded in the fractured vertebra seven studies, 968 participants) and facet joint steroid injection (one study, 217 participants). This Cochrane review is current to November 2017. The cement hardens in the bone space to form an internal cast. Vertebroplasty involves injecting medical-grade cement into a fractured vertebra, under light sedation or general anaesthesia. They can cause severe pain and disability. Osteoporosis is characterised by thin, fragile bones and may result in minimal trauma fractures of the spine bones (vertebrae).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
